Researchers Fabricate Mechanical Metamaterials with Ultra-high Energy Absorption Capacity
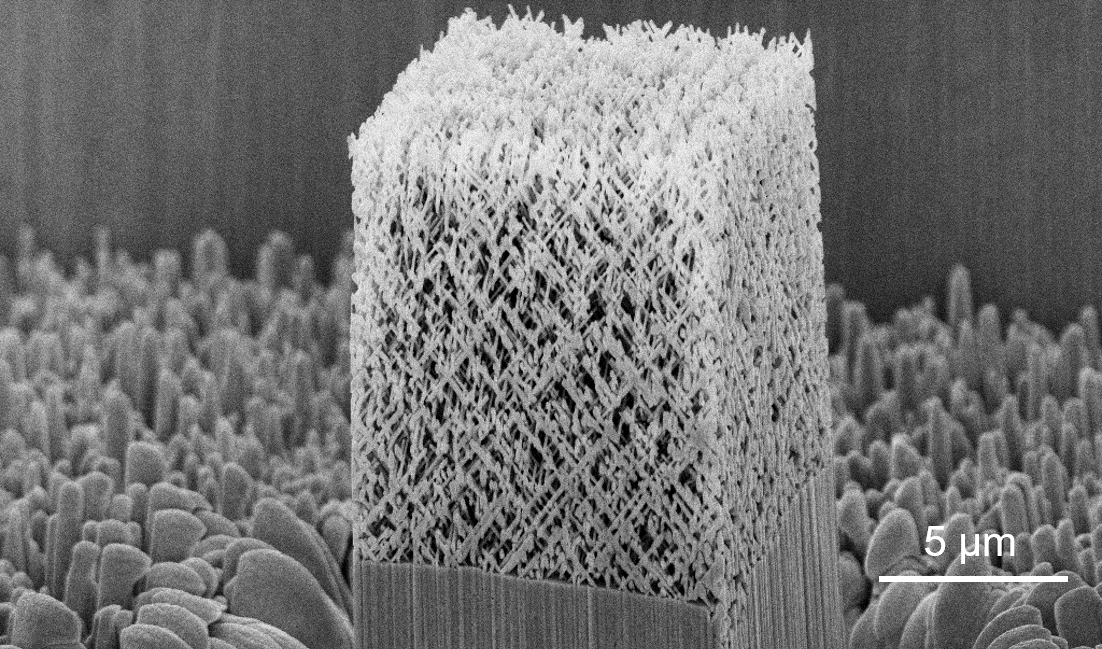
Fig. 1 The SEM image of a FIB-milled quasi-BCC beam nanolattice. (Image from IMP)
Chinese researchers have successfully fabricated mechanical metamaterials with ultra-high energy absorption capacity using the ion track technology. The results were published in Nature Communications as Editors' Highlights.
The study was conducted by the researchers from the Materials Research Center of the Institute of Modern Physics (IMP), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) and their collaborators from Chongqing University.
Mechanical metamaterials refer to a class of composite materials with artificially designed structures, which exhibit extraordinary mechanical properties that traditional materials do not have. Among them, energy absorption mechanical metamaterials can absorb mechanical energy more efficiently, which requires the material itself to equip both high strength and high strain capacity, which, however, hardly co-exist in general.
Nanolattice is a new class of mechanical metamaterials with characteristic sizes on the nanoscale. Due to size effects, geometrical configuration, and material selection, the mechanical properties of this type of porous materials are very different from those of bulk materials. Given its even better mechanical properties with lighter weight, nanolattice is expected to bring revolutionary applications in the field of high-performance functional materials in the future.
Beam-structured nanolattice is the research focus of nanolattice metamaterials. However, it has been so challenging to fabricate metallic beam nanolattice with beam diameter less than 100 nm, and thus its mechanical properties still remain ambiguous.
In this work, based on the Heavy Ion Research Facility at Lanzhou (HIRFL), the researchers fabricated a new type of quasi-body centered cubic (quasi-BCC) beam nanolattice mechanical metamaterial with the ion track technology. The beam diameter of the quasi-BCC nanolattice can be as small as 34 nm, a record-low beam diameter of mechanical metamaterials.
The study demonstrates that gold and copper quasi-BCC beam nanolattices have excellent energy absorption capacity and compressive strength. The experiments show that the energy absorption capacity of the copper quasi-BCC beam nanolattice exceeds that of the previously reported beam nanolattice. In addition, the yield strength of the gold and copper quasi-BCC beam nanolattices exceeds that of the corresponding bulk materials at less than half the density of the latter.
Furthermore, the researchers revealed that the extraordinary mechanical properties are mainly due to the synergistic effect of size effects, quasi-BCC geometry, and good ductility of metals.
The study sheds light on the mechanical properties of the beam nanolattices, and applies the ion track technology as a new method for the exploration of beam nanolattice with ultra-high energy absorption capacity.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Key Research Program of Frontier Sciences, CAS.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-36965-4

Fig. 2 Compression tests on a gold quasi-BCC nanolattice. Scale bars 2 μm. (Image from IMP)

Fig. 3 The Ashby map of energy absorption per unit volume versus density of gold and copper quasi-BCC beam nanolattices and previously reported beam micro/nanolattice metamaterials. (Image from IMP)
Contact :
LIU Fang
Institute of Modern Physics
Email: fangliu@impcas.ac.cn
Contact Information
Institute of Modern Physics
Email: fangliu@impcas.ac.cn



 甘公网安备 62010202000713号
甘公网安备 62010202000713号


