Researchers Develop High-performance Polyimide Separators for Lithium-ion Batteries
Chinese researchers have recently developed a process of fabricating high-temperature resistant polyimide separators for lithium-ion batteries by using the ion track technology.
This study, led by researchers from the Institute of Modern Physics (IMP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), was published in ACS Nano on November 5.
As a critical component of lithium-ion batteries, the separator serves the dual function of isolating the anode and cathode while conducting lithium ions. Its performance is crucial for battery safety and electrochemical efficiency. However, conventional separators, such as polyolefin, exhibit uneven pore structures and limited thermal stability, which can easily lead to shrinkage at high temperatures, causing internal short circuits and triggering thermal runaway.
Polyimide is considered an ideal candidate for high-safety separators due to its excellent thermal stability, high mechanical strength and good chemical stability. Therefore, it is necessary to develop polyimide-based separators with a uniform pore structure.
Utilizing the Heavy Ion Research Facility in Lanzhou (HIRFL), researchers at IMP developed a new preparation process for polyimide ion-track-etched membranes (PITEMs), which could serve as high-safety separators.
Fabricated through the ion-track etching technique, PITEMs possess vertically aligned nanochannels with narrower pore size distribution, which could not only facilitate homogeneous lithium ion transportation, but also ensure the integrity of the separator and the safety of battery at high temperatures.
According to the study, PITEMs could offer distinct advantages compared with traditional polyolefin separators. They exhibit a mechanical strength of up to 150 MPa and excellent high-temperature resistance, with no structural shrinkage even at 450°C.
Lithium/lithium symmetric cells with PITEMs can stably cycle for 1200 hours under conditions of 3 mA per square centimeter, indicating its excellent lithium dendrite suppression capability. Additionally, the graphite/LiFePO4 pouch cells using PITEMs can stably cycle 1000 times at room temperature with a high capacity retention rate, and are capable of normal operation at 150°C.
This study provides new insights into the development of reliable high-performance lithium-ion battery separators with high temperature resistance. The corresponding process is expected to become one of effective methods for enhancing the safety of lithium-ion batteries.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.4c11217
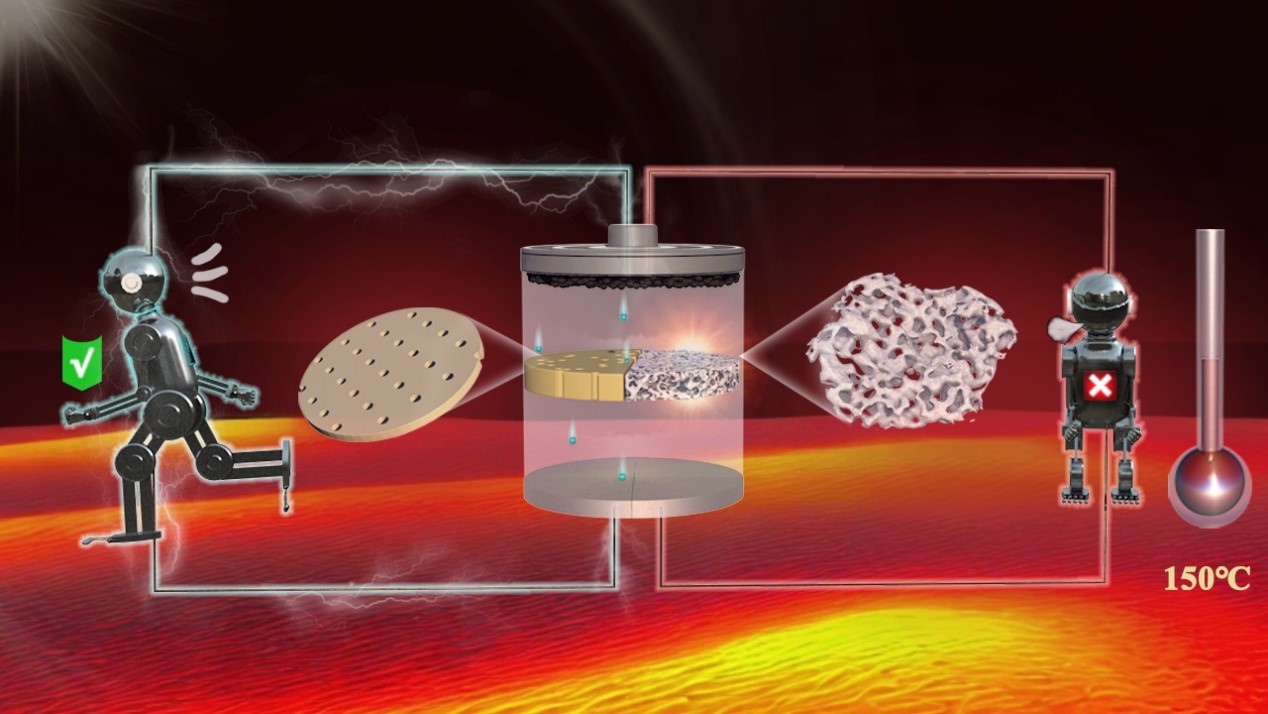
Figure. Schematic diagram illustrating the safety characteristics of PITEMs (left) and conventional polyolefin separators (right) (Image from IMP)
Contact Information
Institute of Modern Physics
Email: LIU Fang



 甘公网安备 62010202000713号
甘公网安备 62010202000713号


