Researchers Obtain New Results on Solar Wind Ion Charge Exchange
The researchers at the Institute of Modern Physics (IMP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) and their collaborators have recently obtained new results on the solar wind ion charge exchange. The results were published in The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series.
Charge exchange is one of the important mechanisms of soft X-ray emission in many celestial environments. Soft X-rays caused by charge exchange are important basic data for diagnosing plasma evolution and celestial plasma modeling, which can be used to study the temperature, abundance, and ion species of solar wind ions or stellar wind ions, and help us gain an in-depth understanding of celestial plasma and fusion.
At present, in charge-exchange soft X-ray emission modeling, researchers usually apply the semi-classical theories to calculate the cross-section data of the state-selective capture resolved by the principal quantum number n and the angular quantum number l. However, the accuracy of the model urgently needs to be verified.
The researchers at IMP and their collaborators used Reaction Microscopy to systematically measure the state-selective charge exchange of Ne(8,9)+ ions with He and H2 in the solar wind speed range, and obtained the cross-section data of the main quantum number resolution of the electron captured to the projectile ion. Researchers then compared the experimental data with the results calculated by the multi-channel Landau-Zener method and found that the main reaction channels were consistent with theoretical expectations.
Meanwhile, by applying charge exchange models commonly used in astrophysics, the researchers obtained the angular quantum number resolution cross-sections corresponding to different angular quantum number distribution models, developed relevant calculation programs, and obtained soft X-ray spectra in the charge exchange between Ne8+ and He atoms. Moreover, researchers compared reconstructed X-ray spectra with the existing X-ray measurement spectrum and found that there were significant differences in different angular momentum distribution models, which tested the applicability of the angular momentum distribution model in astrophysics.
This work is supported by the Key R&D Program of the Ministry of Science and Technology, the Strategic Priority Research Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDB34020000), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
Links to the papers: https://doi.org/10.3847/1538-4365/abd020
https://doi.org/10.7498/aps.70.20201685
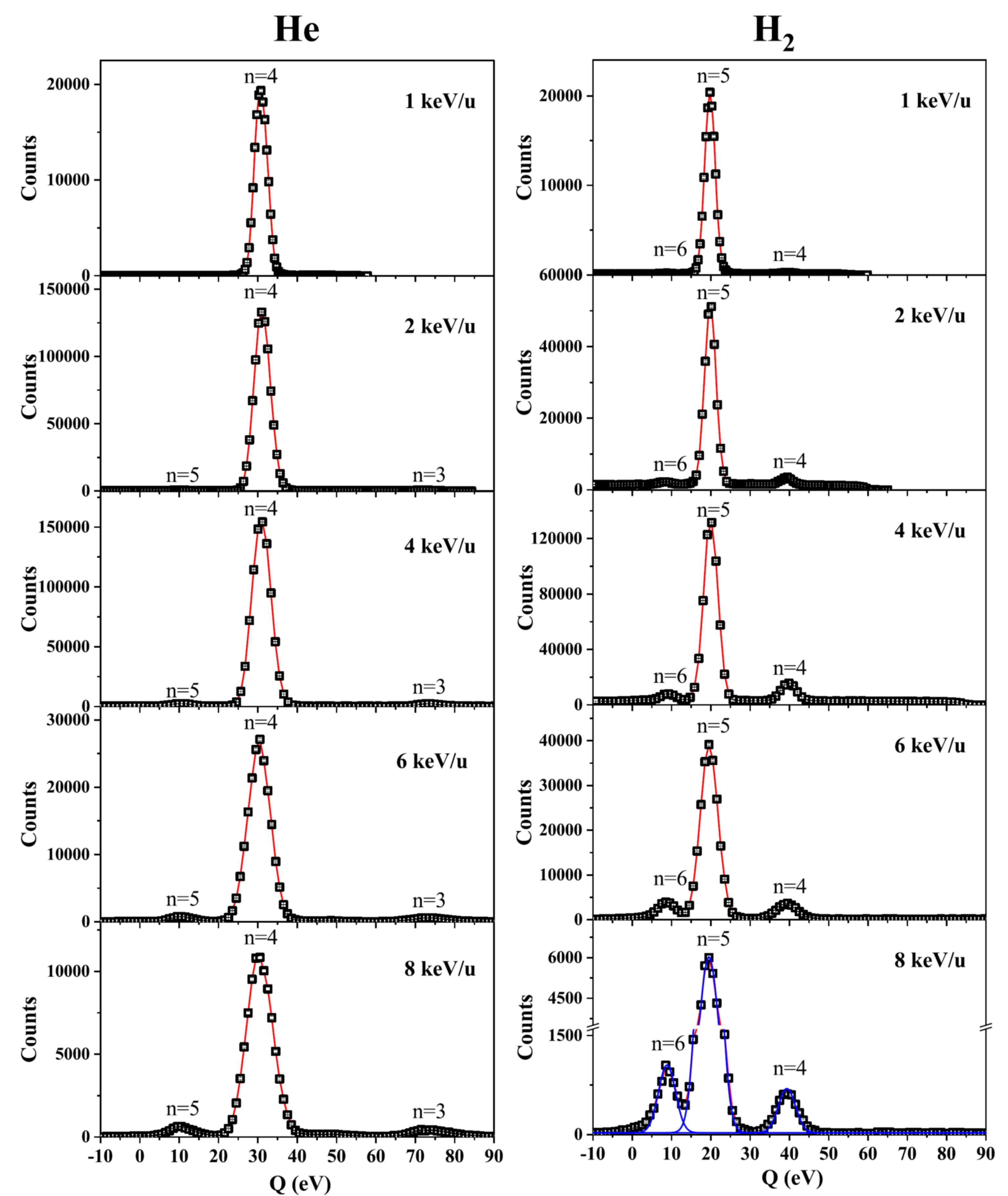
Fig. 1. The measured Q-value spectra for the single electron capture in Ne8+-He collisions at different projectile velocities. (Image from The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series)
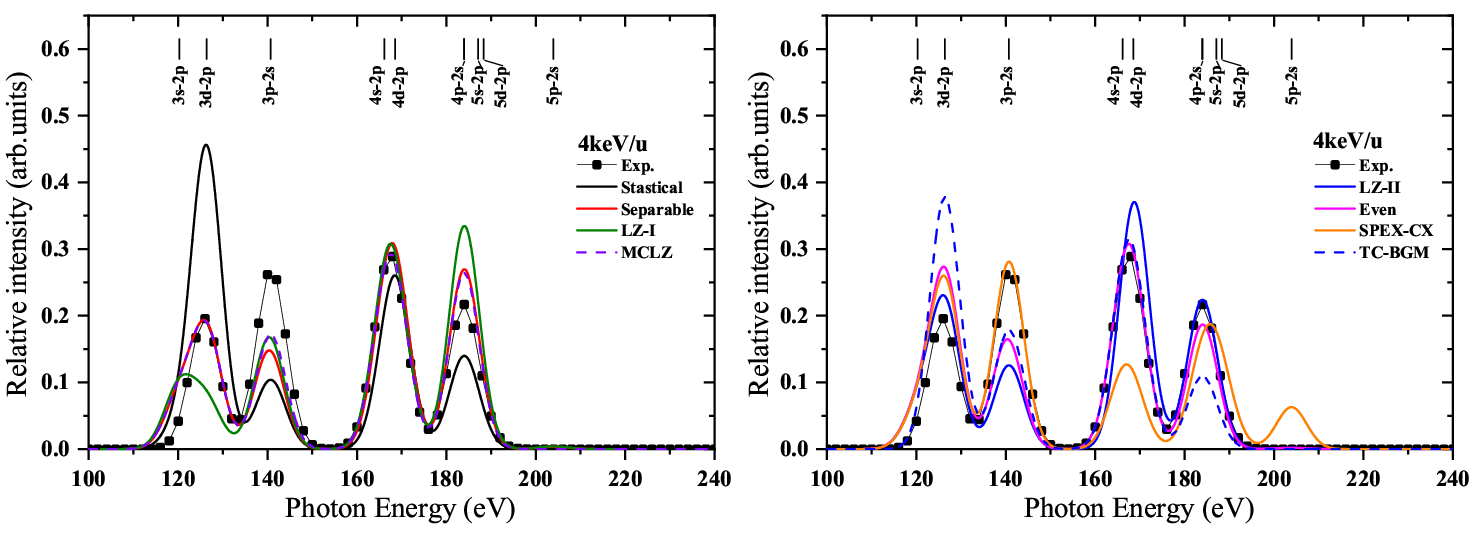
Fig. 2. The normalized emission spectra of Ne7+ following single electron capture between 4 keV/u Ne8+ and He. The solid lines show the reconstructed X-ray spectra from different angular momentum models; The solid square symbol indicates the other group measured X-ray spectra. (Image from The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series)
Contact Information
Institute of Modern Physics
Email: fangliu@impcas.ac.cn



 甘公网安备 62010202000713号
甘公网安备 62010202000713号


