LIBS and its application
Accelerator-driven advanced nuclear energy system (ADANES) proposed by IMP is a closed nuclear energy system, which integrates multiple functions including nuclear waste transmutation, nuclear fuel breeding, and safety power production [1]. Such an advanced system can greatly improve the utilization rate of nuclear fuels, enhance the nuclear safety, reduce the nuclear proliferation. In the system operation, the nuclear waste or fuel related to each stage exists in the loosely packed granular (LPG) form and it is necessary to real-time know the concentrations of some key elements in them that would be helpful for ensuring the system operational quality. Laser induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) has been widely accepted as a promising technology for in-situ multi-component analysis of LPG materials, especially in the radioactive environment of nuclear industry exhibiting unique advantages [2]. Although its attractive advantages have been demonstrated, from the practical viewpoint, the laser-induced plasmas formed from the LPG nuclear wastes and fuels are far from the ideal case as an optical emission source for spectrochemical analysis. The main reasons are as follows. (1) As a kind of typical soft matter, LPG nuclear wastes or fuels absorb a large amount of recoil energy imparted by the plasma formation [3], leading to the ejection of grains and thus resulting in significant degradation of the quality of LIBS signals. (2) The quantitative elemental analysis is extremely difficult due to the fact that the complex composition in nuclear wastes or fuels results in extremely complicated LIBS spectra. The main research topics of the LIBS experiments at IMP will be focused on: i) a detailed understanding for the effects of granular parameters (grain size, grain shape, stacking density, stacking thickness, etc. ) on the LIBS signal from LPG materials; ii) trace elemental analysis of LPG materials with complex composition using LIBS technology combined with machine learning algorithms.
[1] Xuesong Yan, Lei Yang, Xunchao Zhang and Wenlong Zhan, Concept of an Accelerator-Driven Advanced Nuclear Energy System, Energies, 10 (2017) 944.
[2] J. P. Singh and S. N. Thakur, Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy, Elsevier, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007.
[3] J. O. Marston1 and F. Pacheco-Vázquez, Millimetric granular craters from pulsed laser ablation, Phys. Rev. E 99 (2019) 030901.
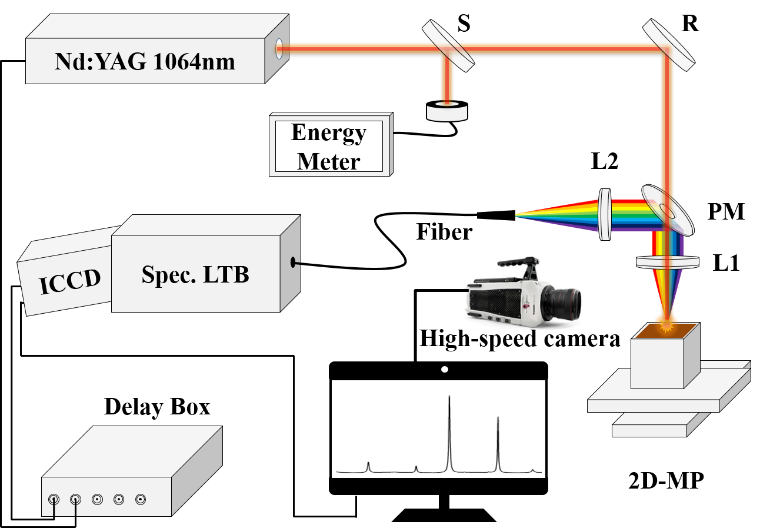
Schematics of the experimental setup for studying the LIBS of LPG materials based on the measurements of spectral emissions and grain ejections.
附件下载: